VQVAE的流程图如下:
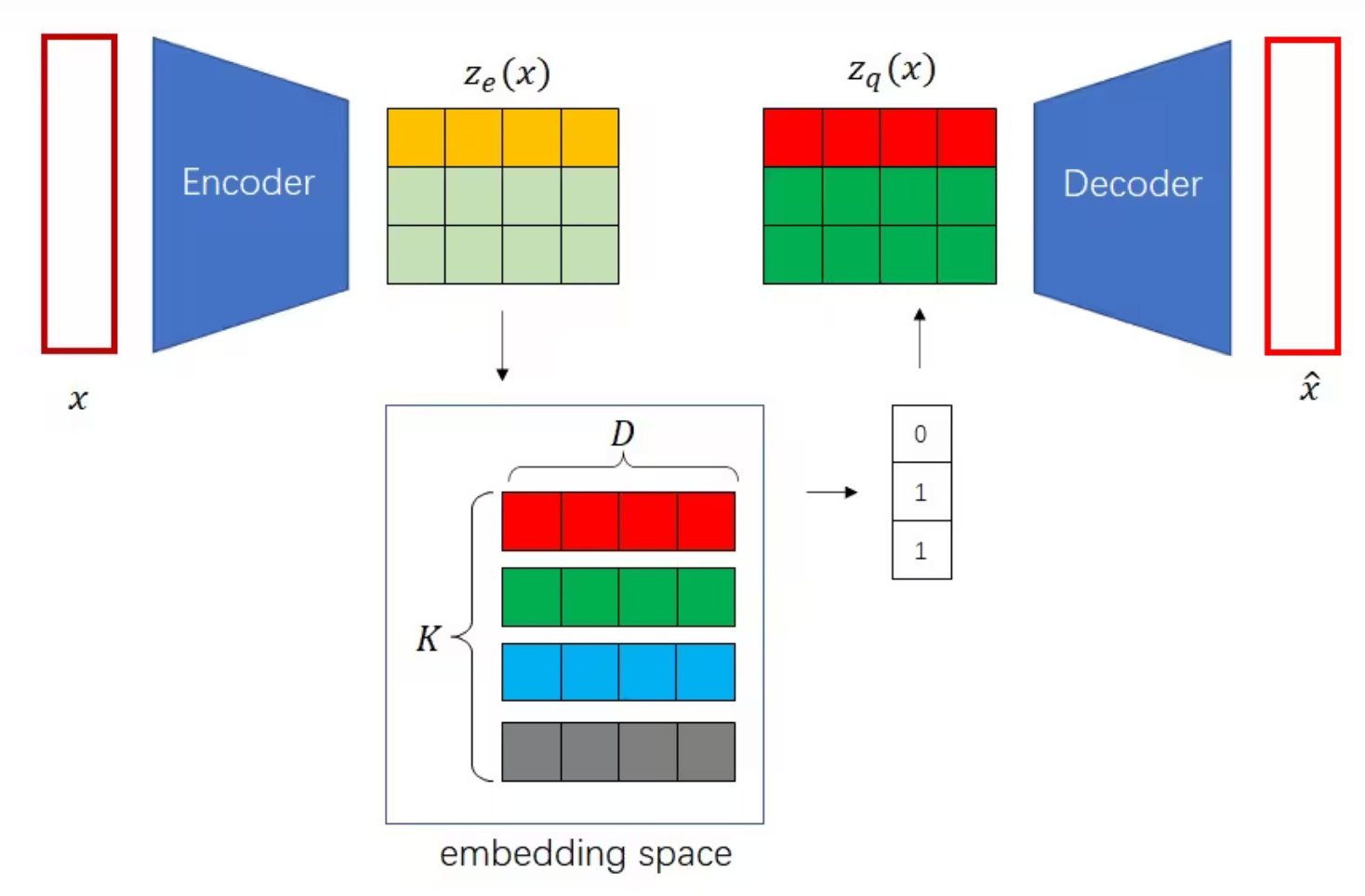
VQVQE的模型搭建如下,其中ResidualBlock是残差块,用于缓解梯度消失和梯度爆炸
class VQVAE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, dim, n_embedding):
super().__init__()
self.encoder = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(input_dim, dim, 4, 2, 1),
nn.ReLU(), nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 4, 2, 1),
nn.ReLU(), nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, 1, 1),
ResidualBlock(dim), ResidualBlock(dim))
self.vq_embedding = nn.Embedding(n_embedding, dim)
self.vq_embedding.weight.data.uniform_(-1.0 / n_embedding,
1.0 / n_embedding)
self.decoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, 1, 1),
ResidualBlock(dim), ResidualBlock(dim),
nn.ConvTranspose2d(dim, dim, 4, 2, 1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.ConvTranspose2d(dim, input_dim, 4, 2, 1))
self.n_downsample = 2然后是模型的前向传播,分为编码,取最近邻,解码
def forward(self, x):
# encode
ze = self.encoder(x)
# ze: [N, C, H, W]
# embedding [K, C]
embedding = self.vq_embedding.weight.data
N, C, H, W = ze.shape
K, _ = embedding.shape
embedding_broadcast = embedding.reshape(1, K, C, 1, 1)
ze_broadcast = ze.reshape(N, 1, C, H, W)
distance = torch.sum((embedding_broadcast - ze_broadcast)**2, 2)
nearest_neighbor = torch.argmin(distance, 1)
# make C to the second dim
zq = self.vq_embedding(nearest_neighbor).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
# stop gradient
decoder_input = ze + (zq - ze).detach()
# decode
x_hat = self.decoder(decoder_input)
return x_hat, ze, zq取最近邻时,我们要用到两块数据:编码器输出ze与嵌入矩阵embedding。ze可以看成一个形状为[N, H, W]的数组,数组存储了长度为C的向量。而嵌入矩阵里有K个长度为C的向量。
为了求N*H*W个向量在嵌入矩阵里的最近邻,我们要先算这每个向量与嵌入矩阵里K个向量的距离。在算距离前,我们要把embedding和ze的形状变换一下,保证(embedding_broadcast - ze_broadcast)**2的形状为[N, K, C, H, W]。我们对这个临时结果的第2号维度(C所在维度)求和,得到形状为[N, K, H, W]的distance。它的含义是,对于N*H*W个向量,每个向量到嵌入空间里K个向量的距离分别是多少。
有了距离张量后,再对其1号维度(K所在维度)求最近邻所在下标,然后就可以从嵌入空间取出最近邻了。由于self.vq_embedding(nearest_neighbor)的形状会是[N, H, W, C]。为了与ze保持一致,要把维度转置。然后使用了梯度停止算子,解码器的输入是zq,但是梯度是直接传给ze的。
nearest_neighbor = torch.argmin(distance, 1)
zq = self.vq_embedding(nearest_neighbor).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
# stop gradient
decoder_input = ze + (zq - ze).detach()MNIST重建图像:

MNIST生成图像:


